Did Someone at the Commerce Dept. Find a SolarWinds Backdoor in Aug. 2020?
On Aug. 13, 2020, someone uploaded a suspected malicious file to VirusTotal, a service that scans submitted files against more than five dozen antivirus and security products. Last month, Microsoft and FireEye identified that file as a newly-discovered fourth malware backdoor used in the sprawling SolarWinds supply chain hack. An analysis of the malicious file and other submissions by the same VirusTotal user suggest the account that initially flagged the backdoor as suspicious belongs to IT personnel at the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), a division of the U.S. Commerce Department that handles telecommunications and Internet policy.

Both Microsoft and FireEye published blog posts on Mar. 4 concerning a new backdoor found on high-value targets that were compromised by the SolarWinds attackers. FireEye refers to the backdoor as “Sunshuttle,” whereas Microsoft calls it “GoldMax.” FireEye says the Sunshuttle backdoor was named “Lexicon.exe,” and had the unique file signatures or “hashes” of “9466c865f7498a35e4e1a8f48ef1dffd” (MD5) and b9a2c986b6ad1eb4cfb0303baede906936fe96396f3cf490b0984a4798d741d8 (SHA-1).
“In August 2020, a U.S.-based entity uploaded a new backdoor that we have named SUNSHUTTLE to a public malware repository,” FireEye wrote.
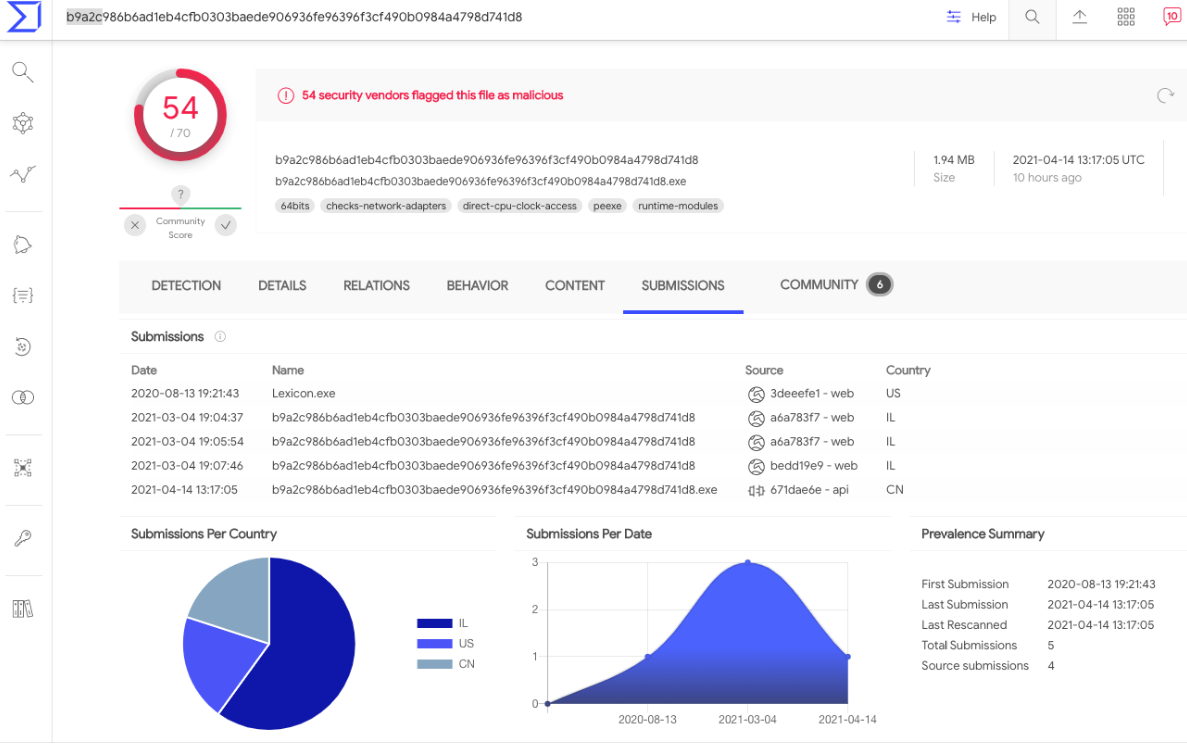
The “Sunshuttle” or “GoldMax” backdoor, as identified by FireEye and Microsoft, respectively. Image: VirusTotal.com.
A search in VirusTotal’s malware repository shows that on Aug. 13, 2020 someone uploaded a file with that same name and file hashes. Premium VirusTotal users can see other files submitted by specific users, and several of those submitted by the same user over nearly two years include messages and files sent to email addresses for people currently working in NTIA’s information technology department.
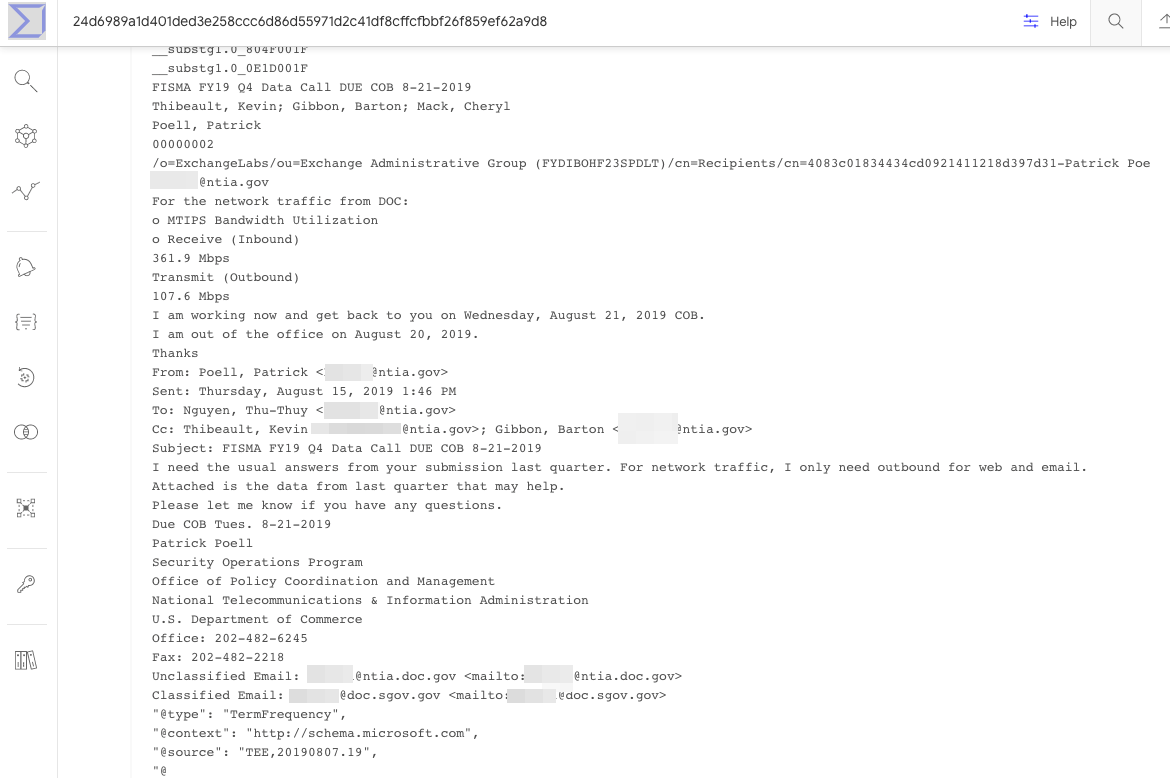
An apparently internal email that got uploaded to VirusTotal in Feb. 2020 by the same account that uploaded the Sunshuttle backdoor malware to VirusTotal in August 2020.
The NTIA did not respond to requests for comment. But in December 2020, The Wall Street Journal reported that the NTIA was among multiple federal agencies that had email and files plundered by the SolarWinds attackers. “The hackers broke into about three dozen email accounts since June at the NTIA, including accounts belonging to the agency’s senior leadership, according to a U.S. official familiar with the matter,” The Journal wrote.
It’s unclear what, if anything, NTIA’s IT staff did in response to scanning the backdoor file back in Aug. 2020. But the world would not find out about the SolarWinds debacle until early December 2020, when FireEye first disclosed the extent of its own compromise from the SolarWinds malware and published details about the tools and techniques used by the perpetrators.
The SolarWinds attack involved malicious code being surreptitiously inserted into updates shipped by SolarWinds for some 18,000 users of its Orion network management software. Beginning in March 2020, the attackers then used the access afforded by the compromised SolarWinds software to push additional backdoors and tools to targets when they wanted deeper access to email and network communications.
U.S. intelligence agencies have attributed the SolarWinds hack to an arm of the Russian state intelligence known as the SVR, which also was determined to have been involved in the hacking of the Democratic National Committee six years ago. On Thursday, the White House issued long-expected sanctions against Russia in response to the SolarWinds attack and other malicious cyber activity, leveling economic sanctions against 32 entities and individuals for disinformation efforts and for carrying out the Russian government’s interference in the 2020 presidential election.
The U.S. Treasury Department (which also was hit with second-stage malware that let the SolarWinds attackers read Treasury email communications) has posted a full list of those targeted, including six Russian companies for providing support to the cyber activities of the Russian intelligence service.
Also on Thursday, the FBI, National Security Agency (NSA), and the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Administration (CISA) issued a joint advisory on several vulnerabilities in widely-used software products that the same Russian intelligence units have been attacking to further their exploits in the SolarWinds hack. Among those is CVE-2020-4006, a security hole in VMWare Workspace One Access that VMware patched in December 2020 after hearing about it from the NSA.
On December 18, VMWare saw its stock price dip 5.5 percent after KrebsOnSecurity published a report linking the flaw to NSA reports about the Russian cyberspies behind the SolarWinds attack. At the time, VMWare was saying it had received “no notification or indication that CVE-2020-4006 was used in conjunction with the SolarWinds supply chain compromise.” As a result, a number of readers responded that making this connection was tenuous, circumstantial and speculative.
But the joint advisory makes clear the VMWare flaw was in fact used by SolarWinds attackers to further their exploits.
“Recent Russian SVR activities include compromising SolarWinds Orion software updates, targeting COVID-19 research facilities through deploying WellMess malware, and leveraging a VMware vulnerability that was a zero-day at the time for follow-on Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication abuse,” the NSA’s advisory (PDF) reads. “SVR cyber actors also used authentication abuse tactics following SolarWinds-based breaches.”
Officials within the Biden administration have told media outlets that a portion of the United States’ response to the SolarWinds hack would not be discussed publicly. But some security experts are concerned that Russian intelligence officials may still have access to networks that ran the backdoored SolarWinds software, and that the Russians could use that access to affect a destructive or disruptive network response of their own, The New York Times reports.
“Inside American intelligence agencies, there have been warnings that the SolarWinds attack — which enabled the SVR to place ‘back doors’ in the computer networks — could give Russia a pathway for malicious activity against government agencies and corporations,” The Times observed.
>>More
