‘BlueLeaks’ Exposes Files from Hundreds of Police Departments
Hundreds of thousands of potentially sensitive files from police departments across the United States were leaked online last week. The collection, dubbed “BlueLeaks” and made searchable online, stems from a security breach at a Texas web design and hosting company that maintains a number of state law enforcement data-sharing portals.
The collection — nearly 270 gigabytes in total — is the latest release from Distributed Denial of Secrets (DDoSecrets), an alternative to Wikileaks that publishes caches of previously secret data.
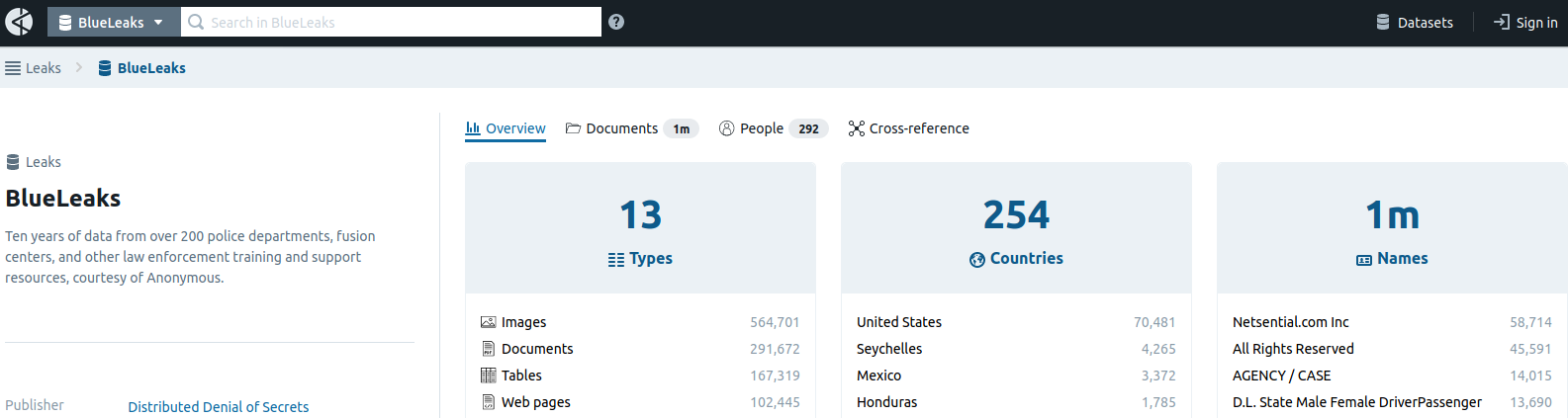
In a post on Twitter, DDoSecrets said the BlueLeaks archive indexes “ten years of data from over 200 police departments, fusion centers and other law enforcement training and support resources,” and that “among the hundreds of thousands of documents are police and FBI reports, bulletins, guides and more.”
Fusion centers are state-owned and operated entities that gather and disseminate law enforcement and public safety information between state, local, tribal and territorial, federal and private sector partners.
KrebsOnSecurity obtained an internal June 20 analysis by the National Fusion Center Association (NFCA), which confirmed the validity of the leaked data. The NFCA alert noted that the dates of the files in the leak actually span nearly 24 years — from August 1996 through June 19, 2020 — and that the documents include names, email addresses, phone numbers, PDF documents, images, and a large number of text, video, CSV and ZIP files.
“Additionally, the data dump contains emails and associated attachments,” the alert reads. “Our initial analysis revealed that some of these files contain highly sensitive information such as ACH routing numbers, international bank account numbers (IBANs), and other financial data as well as personally identifiable information (PII) and images of suspects listed in Requests for Information (RFIs) and other law enforcement and government agency reports.”

The NFCA said it appears the data published by BlueLeaks was taken after a security breach at Netsential, a Houston-based web development firm.
“Preliminary analysis of the data contained in this leak suggests that Netsential, a web services company used by multiple fusion centers, law enforcement, and other government agencies across the United States, was the source of the compromise,” the NFCA wrote. “Netsential confirmed that this compromise was likely the result of a threat actor who leveraged a compromised Netsential customer user account and the web platform’s upload feature to introduce malicious content, allowing for the exfiltration of other Netsential customer data.”
Reached via phone Sunday evening, Netsential Director Stephen Gartrell declined to comment for this story.
The NFCA said a variety of cyber threat actors, including nation-states, hacktivists, and financially-motivated cybercriminals, might seek to exploit the data exposed in this breach to target fusion centers and associated agencies and their personnel in various cyber attacks and campaigns.
The BlueLeaks data set was released June 19, also known as “Juneteenth,” the oldest nationally celebrated commemoration of the ending of slavery in the United States. This year’s observance of the date has generated renewed public interest in the wake of widespread protests against police brutality and the filmed killing of George Floyd at the hands of Minneapolis police.
Stewart Baker, an attorney at the Washington, D.C. office of Steptoe & Johnson LLP and a former assistant secretary of policy at the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, said the BlueLeaks data is unlikely to shed much light on police misconduct, but could expose sensitive law enforcement investigations and even endanger lives.
“With this volume of material, there are bound to be compromises of sensitive operations and maybe even human sources or undercover police, so I fear it will put lives at risk,” Baker said. “Every organized crime operation in the country will likely have searched for their own names before law enforcement knows what’s in the files, so the damage could be done quickly. I’d also be surprised if the files produce much scandal or evidence of police misconduct. That’s not the kind of work the fusion centers do.”
>>More